DAO – The Future of Organizations?
Decentralization is the new standard and norm for the future of the internet – web3 and metaverse, we’re moving towards, and DAO will be an integral part of this future.
Imagine being able to run an entire organization of people without any central authority.
Imagine no conflict of priorities among stakeholders and members.
Imagine the perfect system for distributing income and profits equally.
Thanks to DAOs, you don’t have to imagine this anymore. It’s all possible, and it’s already happening. However, much like anything, it has its limitations too.
In this article, you’ll find out –
- What are DAOs, and how do they work?
- DAO vs Traditional Organizations
- Are DAOs Taxable?
- Limitations of DAOs.
What is a DAO?
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO) are built on smart contracts – self-executing tasks and contracts set up in a code. They are fully autonomous, public, transparent and have no central authority.
Unlike traditional organizations, where only a selected group of people are allowed to see behind the curtains, anyone can view and audit the underlying code of a DAO since the smart contracts are usually open source.
As the name suggests, these organizations are run and governed by their own members. No third party dictates its actions and decisions.
The members will decide the next step for the organization, upgrades, treasure allocations and other critical governing decisions.
To take part in the governance of a DAO, you’ll have to buy its tokens.
It has two functions – first, by buying its tokens, you’re adding liquidity to its treasury. Second, by buying tokens, you’ll have a say in the governance decisions.
Different DAOs have different tokenomics, but generally, the more tokens you have, the more governance power or options you get.
Usually, a few stakeholders with the most governing power will create different proposals, which the rest of the members can then vote on. The one with the most votes will determine how the organization moves forwards.
How Does it Work?
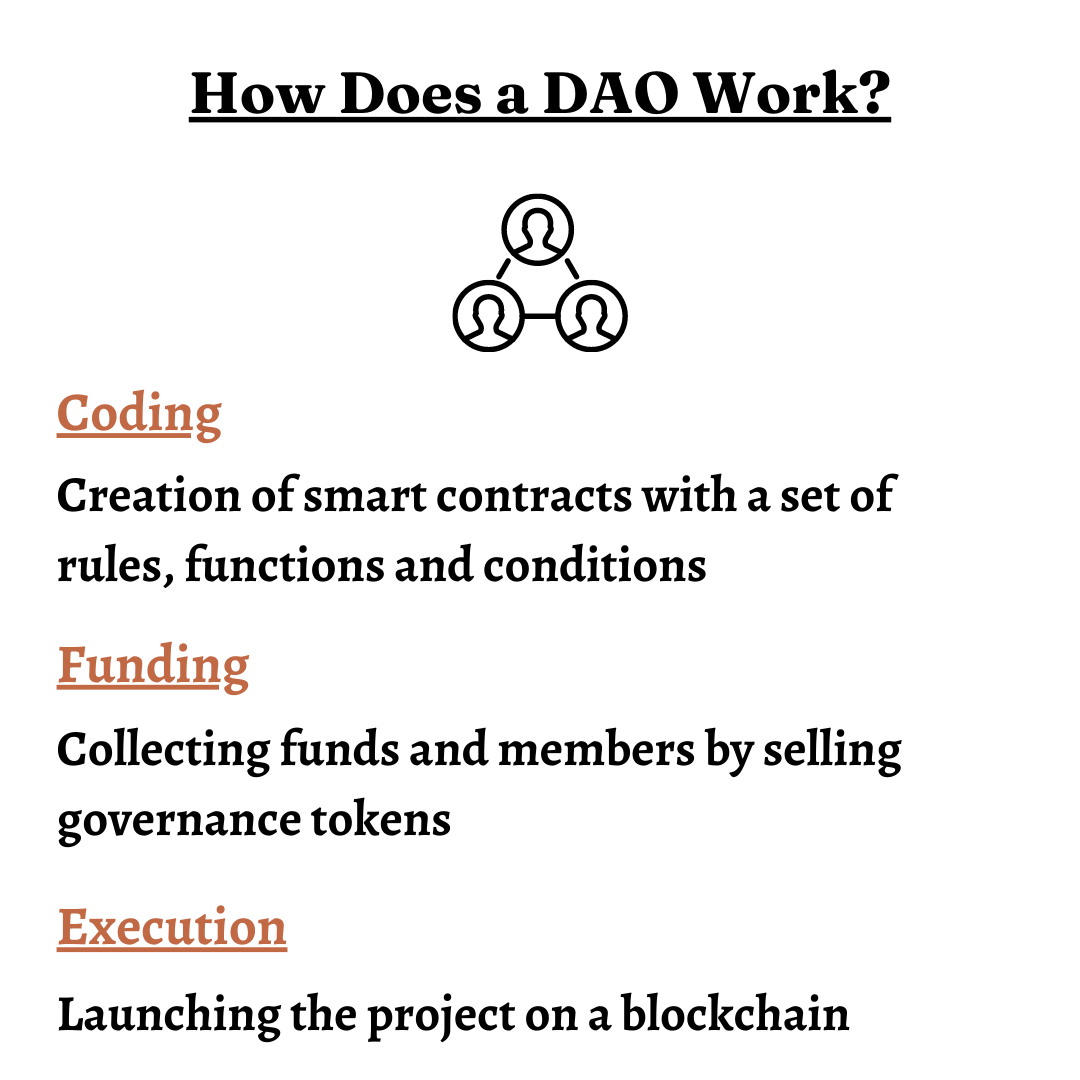
There are three stages to successfully executing a DAO –
Coding: The first stage is the development stage.
In this stage, a group of developers will come together to create the foundational framework of the organization.
How do they do it?
By creating a smart contract with a set of rules and functions.
As we mentioned before, the smart contract is open source, which means anyone can view it, verify it and decide if the project is something they would like to be involved with.
Funding: The next stage of the process is to allocate funds.
Most DAOs do this by selling tokens.
Each token has a certain amount of voting power attached to it. So, people are basically paying for how much say they wish to have in the governance decisions.
In the process, the project is getting funded and, at the same time, gathering community members.
Different DAOs have different functions. Hence, they all gather funds for different goals.
Some projects do it to make group investments in NFTs or other cryptocurrencies. Some do it purely just for profits. Some do it to grow their project or community, while some do it for a greater cause.
Execution: This is the final stage of the process.
After stages one and two, the project is finally launched on a blockchain.
Once it’s launched, the smart contract is permanent. It can’t be changed, edited or altered by anyone, even the developers.
The only way to change something is to create a new smart contract and move all the members and treasury to the new ones. That also requires a collective agreement of all members and stakeholders.
How is DAO Different from Traditional Organizations?
The most common problem we see in traditional organizations is the conflict of priorities and values. Usually, this conflict occurs between the CEO or any other person at the top position and stakeholders, where one person’s decision can negatively impact another person’s interests.
As a result, we often see board members forcing the CEO to do something that they may not wanna do or the CEO doing something that hurts the company stocks, hence the stakeholders.
The recent hostile takeover of Twitter by Elon Musk is a perfect example.
The most beautiful thing about DAOs is that everyone acts in the best interest of the community or organization.
The only way the members in a DAO can profit is if it achieves its goals. Therefore, everyone has an aligned interest, and acting against it is against their own self-interest. And who would do that?
Are DAOs Taxable?

Taxation around DAOs is just as complex as its legality, which we’ll discuss in the next section.
On an individual level, we know that you still pay capital gains taxes on selling your governance token.
And income taxes on selling any product or services for crypto or fiat currency.
However, we don’t know if DAO, as an entity, is taxable or not. If we go by the existing framework that we already have, almost all DAO qualifies as a taxable entity.
But the problem is – who does the IRS tax?
There’s no central authority or a top guy in a DAO. So, who will file the taxes? Who does the IRS hold accountable?
Until the IRS releases proper guidelines around DAOs and their taxation, this is all we know – capital gains taxes on selling governance tokens and income taxes on selling products or services.
Also, check out our guide to crypto taxes.
Drawbacks of DAO
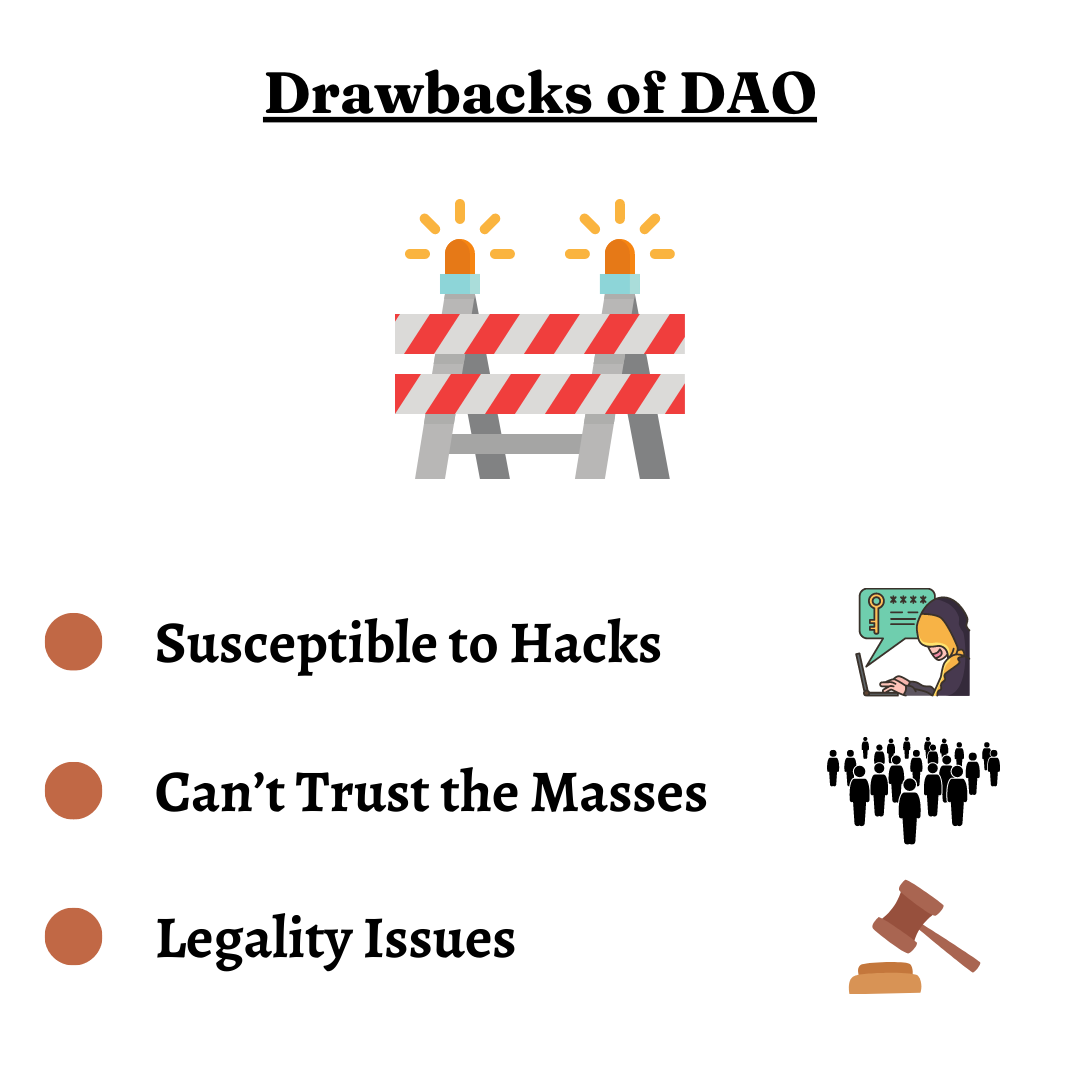
Susceptible to Hacks – The first DAO that ever launched, The DAO, was also hacked and later closed.
The threat of hacking and exploitation is a real problem in DAOs. Any loopholes or shortcomings in the smart contract are permanent.
As we discussed, by the time someone notices it, creates a proposal to move the project to a new smart contract and conducts voting, it may be too late.
Can’t Trust the Masses – Many financial and economic experts believe it’s not the best idea to trust the masses to decide what’s best for a group or community, especially in terms of finance.
Legality Issues – Since all members of a DAO own the organization, any legal consequence or action against or involving the organization can get highly complex due to different regional laws and governments.
No country has specified any guidelines yet regarding how DAOs will be regulated.
Some Promising and Unique Projects
SharkDAO – A community that works together to acquire NFTs.
Proof Of Humanity – A DAO focused on creating a new identity system and distributing Universal Basic Income (UBI).
DAOhaus – This DAO allows you to create and launch your own DAOs.
ConstitutionDAO – The ConsititutionDAO communities raised $47 million to buy a piece of the American constitution but lost to a bid of $43.2 million.
Decentraland DAO – Decentraland is a virtual world where you can buy, sell and rent lands and do almost anything you want, along with millions of other users.